Speaker
Description
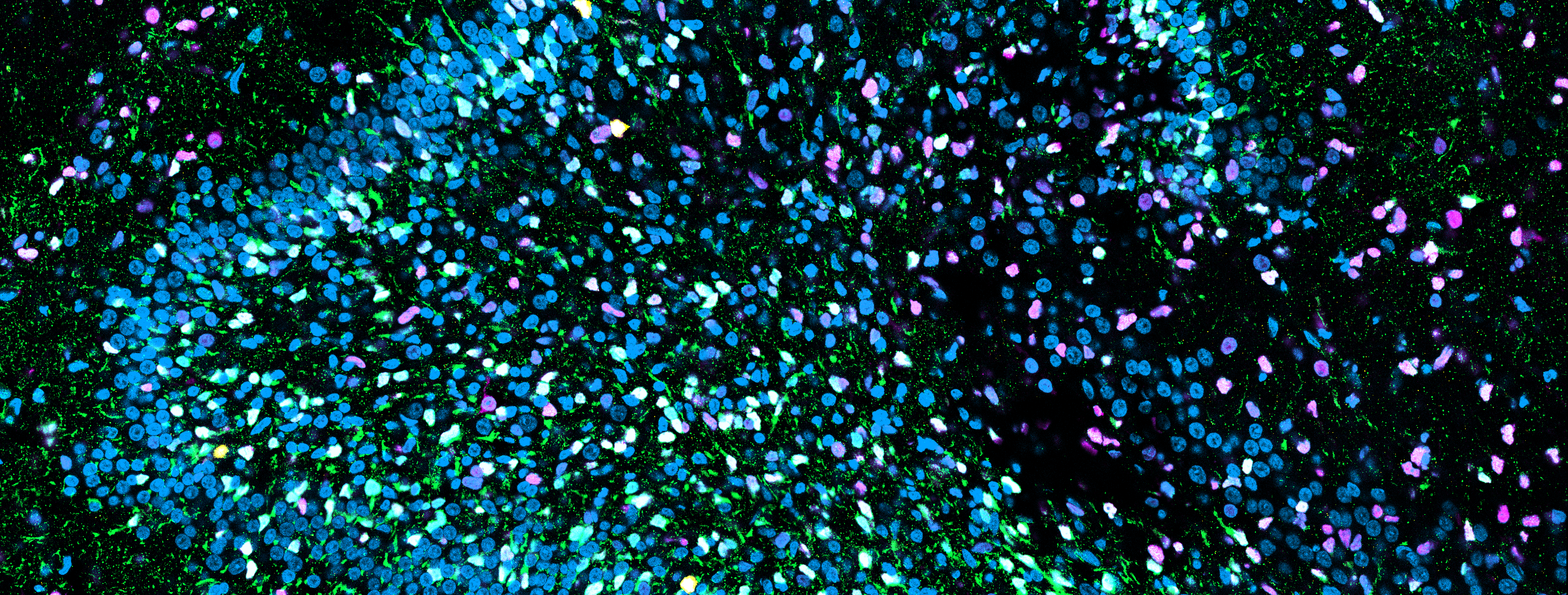
Cohen syndrome (CS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by a biallelic mutation in the VPS13B gene. It is a heterogeneous genetic disorder characterized by microcephaly, hypotonia, intellectual disability, neutropenia, and retinal degeneration. VPS13b is localized at the Golgi apparatus and is essential for the maintenance of organelle architecture. To understand how VPS13b mutation affects cortical development, we use cortical organoids as an in vitro model. We are electroporating a Sh construct against VPS13B at D39 and analyzing after 4 div or 7 div. By analyzing the samples, we were able to see defects in migration and an increase in TBR2+ intermediate progenitors. Further, we generate cortical organoids from iPSCs reprogrammed from CS patient’s fibroblast. Initial results show defects in Golgi integrity and endosomal vesicles. We are following up on these observations to understand the effects of these defects on the secretory pathway, cortical development, and neuronal maturation. Moreover, we are using in utero electroporation, electroporating Sh Vps13b in the cortex of mouse embryos at E15.5 and analyzing postnatally at P5 to investigate the role Vps13b has on neurogenesis in vivo. We intend to combine different omics approaches, live imaging on organoids and clearing to investigate the underlying molecular mechanism VPS13b exerts during cortical development.
| Author(s) | Salma Amin1*, Elena Restelli, Reyhaneh Azizi, Luisa Sturiale2, Domenico Garozzo3, Rita Barone2,4, Elena Taverna1 |
|---|---|
| Affiliation(s) | "1Human Technopole, Milan, Italy. 2CNR, Istituto per i Polimeri, Compositi e i Biomateriali Catania, Catania, Italy. 3CNR, Istituto per i Polimeri, Compositi e i Biomateriali Catania, Catania, Italy. 4Pediatric Neurology Unit, Department of Pediatrics, University of Catania, Catania, Italy." |