Speaker
Description
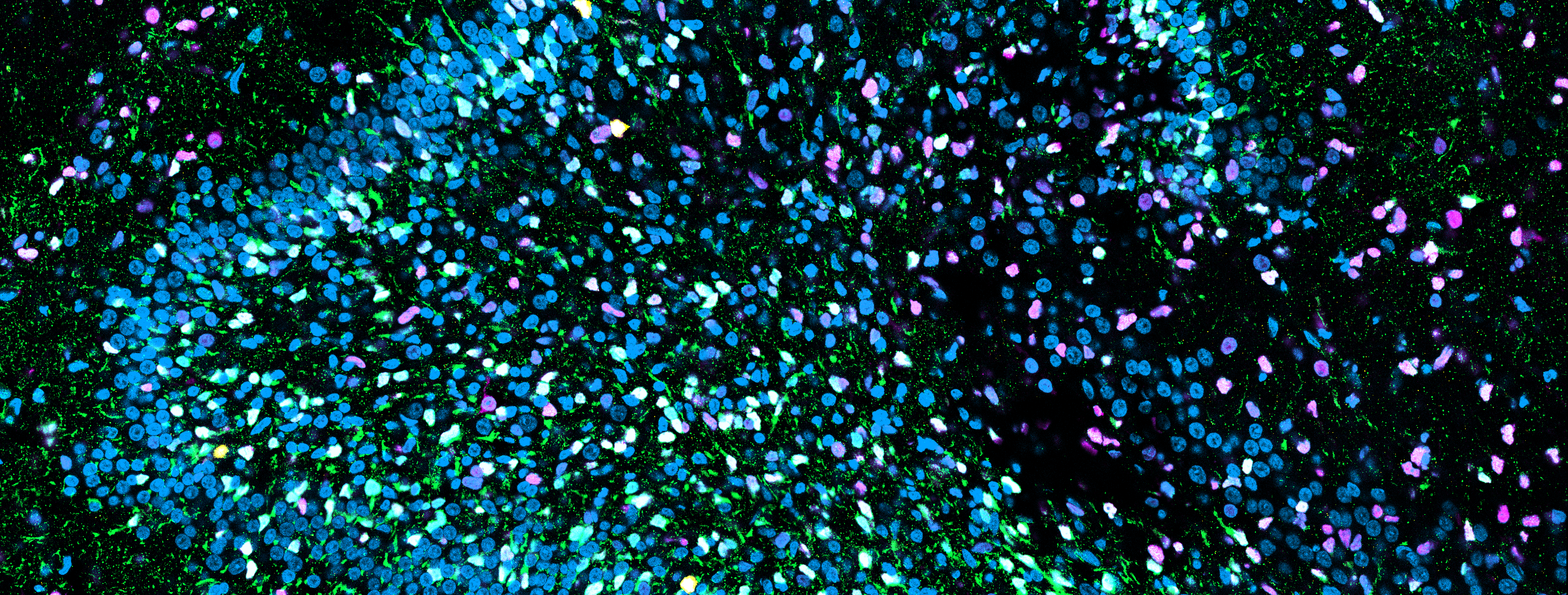
TMEM151A, an almost unknown gene, has been recently associated to Paroxysmal Kinesigenic Dyskinesia (PKD), an autosomal dominant movement disorder. Our project aims to identify the role of TMEM151A in the brain from both a physiological and pathological point of view through a multi-level approach. We studied the topology of TMEM151A and showed that it is a membrane protein with two membrane-spanning helices and a large cytosolic domain with alpha-helix and beta-sheet structures. We explored TMEM151A expression from macro-areas of the brain down to the cellular level by real-time PCR experiments and showed that it is enriched in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and spinal cord. In primary neuronal cultures TMEM51A is developmentally regulated with a peak of expression between 14 and 21 days in vitro, a time of intense synaptogenesis. Overexpression experiments showed an enrichment in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. To go in depth about the role of TMEM151A in the disease, we investigated the effects of some pathological mutations by in vitro assays. We show that some of them cause alteration in the protein expression, suggesting a possible loss of function mechanism. Therefore, to mimic the pathology, we used induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) carrying a null mutation in TMEM151A. KO-TMEM151A iPSCs and isogenic control have been differentiated to glutamatergic excitatory neurons and functional characterization is ongoing. To define the molecular interactome of TMEM151A in mouse brain, we used a pull down-based proteomic approach and identified several potential interacting proteins involved in membrane trafficking processes. We are validating these potential candidates by biochemical approaches. Our results may help to understand the physio-pathological mechanisms at the basis of these paroxysmal disorders and to get a step forward for the identification of new targeted therapeutic strategies.
| Author(s) | *Lisastella Morinelli 1-2, M. Muià 1, M. Bartolucci 3, M. Servetti 1-2, L. Ferrera 4, B. Corradi 1-2, P. Arnaldi 1-7, K. Cortese 1, L. Muzzi 6, L. Maragliano 2-5, A. Petretto 3, F. Zara 4-6, B. Sterlini 1-7, A. Corradi 1-7 |
|---|---|
| Affiliation(s) | 1University of Genova - Department of Experimental Medicine – Genova- Italy, 2Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia - Center for Synaptic Neuroscience and Technology – Genova - Italy, 3IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini - Core Facility for Omics Sciences – Genova - Italy, 4IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini - Unit of Medical Genetics – Genova - Italy, 5Polytechnic University of Marche - Department of Life and Environmental Sciences – Ancona - Italy, 6University of Genova, Department of Neurosciences Rehabilitation Ophthalmology Genetics Maternal and Child Health – Genova - Italy, 7IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino – Genova - Italy |